Organizations are looking to their vast data stores for nuggets of information that give them a leg up on their competition. “Big Data Analytics” and Artificial Intelligence are the technologies promising to find those gold nuggets. Mining data is accomplished through a “Distributed Data Lake Architecture” that enables cleansing, linking, and analytics of varied distributed data sources.
Show Notes
Ad Hoc Data Management
- Data is generated in several locations in your organization.
- IoT (Edge Devices) has increased the number of locations and types of data that have grown.
- Organizations typically look at the data sources individually and application-centric.
- Data Scientists look at a data source and create value from it. One application at a time.
- Understanding the data and normalizing it is key to making this successful. (A zip code is a zip code, a phone number has multiple formats, Longitude, Latitude)
- Overhead of creating a Data-Centric Application is high if you start from scratch.
- People begin using repeatable applications to get the benefits of reuse.
Data Warehouse Architecture
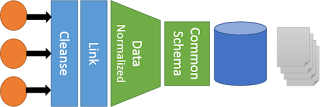
- Data Warehouse architecture takes repeatable processes to the next level. Data is cleansed, linked, and normalized against a standard schema.
- Data is cleansed once and used several times, with different applications.
- Benefits include:
- Decrease time to answer.
- Increase reusability
- A decrease in Capital Cost
- Increase in Reliability
Data Lake Architecture
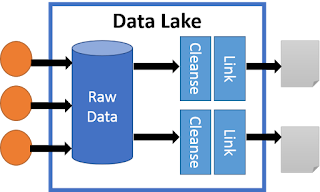
- A Data Lake moves all of the data and stores all of the data in its raw format.
- Data Lake Architecture uses Meta-Data to better understand the data.
- Allows for late binding of applications to the data.
- Gives the ability to use/see the data in different ways for different applications.
- Benefits include:
- Ability to reuse data for more than one purpose
- Decrease time to create new applications
- Increase the reusability of data
- Increase Data Governance (Security and Compliance)
Distributed Data Lake (Data Mesh)
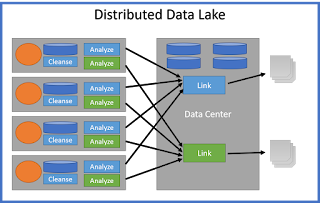
- One of the biggest problems with Data Lake and Data Warehouse is the movement of data.
- As data volume goes up, so does its gravity. It becomes harder to move.
- Regulations can limit where the data can actually reside.
- Edge devices that have data need to encrypt and manage data on edge devices before pushing to a data lake.
- This architecture allows for data services to be pushed to compute elements into the edge. Including storage, encryption, cleanse, link, etc..
- Data is only moved to a centralized location based on policy and data governance.
- Each application developed does not need to know where the data is located. The architecture handles that for them.
- Benefits include:
- Decrease time to answer.
- Late data binding to runtime.
- Multiple applications running on the same data in the same devices
- Decrease cost due to decrease movement of data.
What is Rise of the Stack Developer?
DevOps is all the rage right now. It is meant to bridge the gap between Software Development and IT. But I think we are still missing something who is building reusable stacks that software development can use over and over again. As microservices gain momentum, the importance of the Stack Developer becomes important. This group will explore the "Best Practices" of this rising new position.